Analysis of the piezoelectric effect of crystals
Piezoelectric Effect of Crystals
In 1881, they verified the inverse piezoelectric effect through experiments and obtained the forward and inverse piezoelectric constants.
Principle of piezoelectric effect: If pressure is applied to a piezoelectric material, it will produce a potential difference (called the positive piezoelectric effect).
When certain dielectrics in the crystal are deformed by external forces in a certain direction, polarization will occur inside them, and at the same time,
opposite positive and negative charges will appear on its two opposite surfaces. The quartz crystal used inside the passive crystal oscillator
has the physical properties mentioned above. Such crystals are collectively referred to as piezoelectric crystals. If pressure is applied to a slice
(quartz wafer) cut from a quartz crystal in a certain direction, an electric charge will be generated on this slice. If the slice is stretched in the opposite direction,
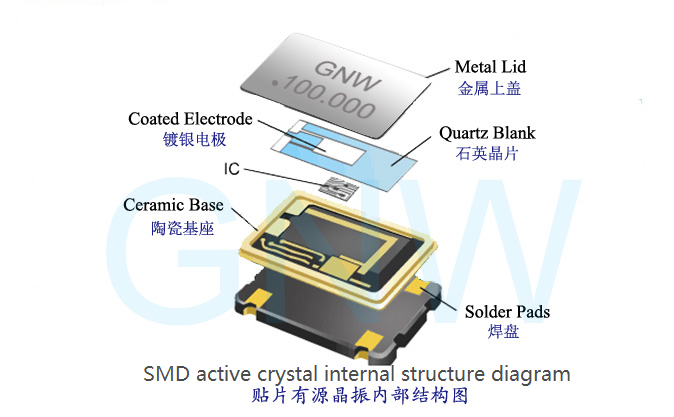
charges will also appear on the slice, but with the opposite sign. The active crystal oscillator is equipped with a stable built-in circuit. After power on,
a stable alternating electric field is applied to the crystal, and the active crystal oscillator will output a signal.
However the passive crystal oscillator requires an external circuit, which results in that the electric field applied to the crystal is not as stable and matched as the active crystal oscillator.
Therefore, the signal output by an active crystal oscillator is more stable than a passive crystal oscillator.
