Crystal oscillator selection: The solutions of crystal frequency deviation and temperature drift
In the actual circuit application, we often encounter two kinds of problems: one is the crystal oscillator in the circuit match is not ideal,
affecting the use of the effect; the second is the crystal oscillator temperature drift is too large, or even affect the performance of the product.
The reason for this is that crystal oscillators are divided into two categories: passive and active.
The effect of using passive crystal oscillator not only depends on its own electrical parameters,
but also has a great correlation with the design matching of the oscillation circuit. So there are often match is not ideal condition.
Active crystal oscillator is provided to the users directly after the quartz crystal and IC have been debugged to the optimum state.
This can avoid the problem of frequency deviation in the circuit caused by improper load matching of the passive crystal on the client side.
The frequency accuracy of passive crystal oscillator is affected by two characteristics inherent to quartz crystals themselves:
frequency tractions and temperature drift.
Frequency tractions:
A physical quantity that refers to the change in frequency accuracy of a quartz crystal as the load capacitance changes.( PPM/PF)
Temperature drift:
It is a physical quantity that changes with the temperature of the quartz crystal, which is an inherent characteristic of quartz crystal,
and its frequency-temperature curve is related to the cutting type and cutting angle of the quartz wafer. From the user's point of view,
the user is unable to change the cutting angle and cutting type of the wafer, but it is easy to change the load of the oscillation return.
For this reason, when using passive crystal oscillator, customers are prone to frequency deviation caused by the load mismatch.
Active crystal oscillator is highly accurate and stable because of the use of professional oscillation chip inside them.
Before the active crystal oscillator is packaged, the crystal manufacturer changes the thickness of the chip by spraying silver
or etching the electrodes on the quartz chip, thus achieving fine tuning of the crystal frequency.
From this way, the oscillation circuit can not only output the desired target frequency,
but also avoid the frequency drift caused by the load mismatch, which greatly improves the frequency signal accuracy of the oscillation circuit.
Temperature drift is an important characteristic of quartz crystals.
All crystal products made of quartz crystal material have a certain temperature drift,
so the temperature drift becomes an important factor affecting the frequency accuracy of crystal oscillators.
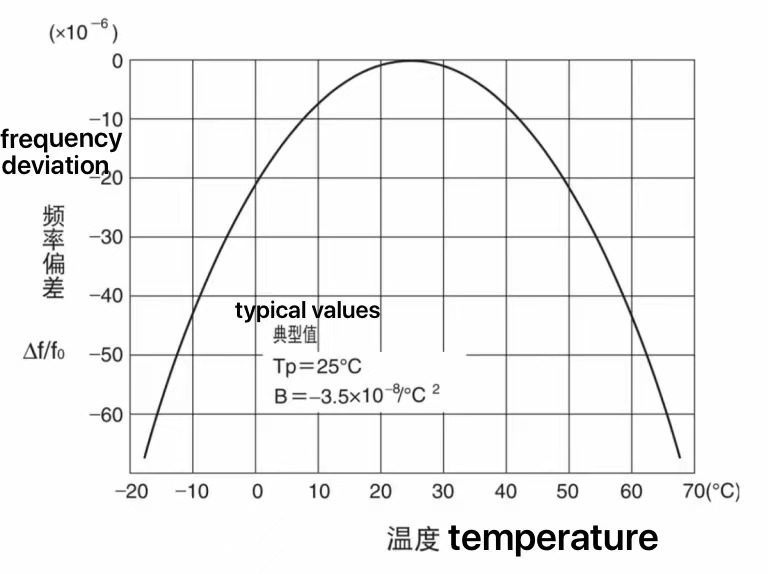
Tuning fork passive 32.768 khz crystal oscillator as the working temperature deviates from the normal temperature of 25 ℃,
the temperature drift also becomes larger. If you need an industrial grade crystal oscillator(-40℃~85℃) with a temperature spread control of ±30ppm or less,
using a normal tuning fork passive 32.768 khz crystal oscillator will not meet the requirements.
However, if the quartz wafer cut type can be changed to AT cut, then the industrial grade temperature spread within ±30ppm will not be a problem.

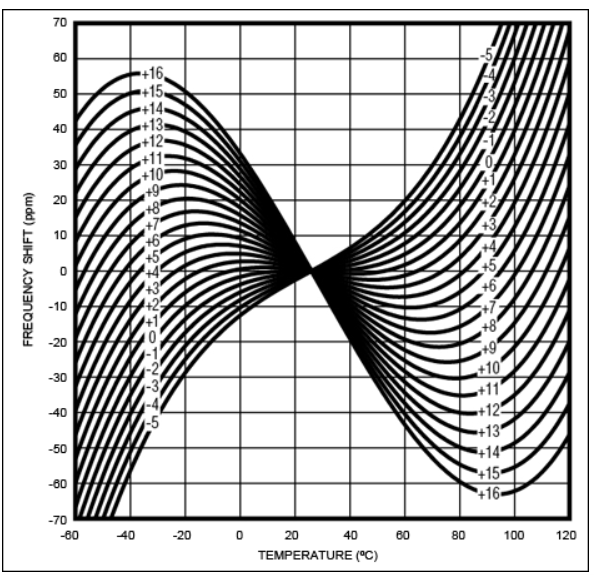
As we all know, the AT-cut quartz crystal frequency temperature curve is a three-dimensional curve,
lying in an "S" curve. When the temperature is between -10°C and +60°C, there are two "inflection points",
where the temperature drift turns back in the opposite direction. Therefore,
as long as the control angle of the wafer is within a certain tolerance,
it is not difficult to ensure that the temperature drift of the two inflection points does not exceed ±30ppm at -40℃~85℃.
Measures:
一.Replacing conventional tuning fork quartz chips with photolithography
This technology is mainly applied to passive SMD 32.768 khz crystal oscillator the mainstream package is FC-135/SMD3215.
二.Dividing frequency technology
The active 32.768 khz crystal oscillator can be achieved by dividing the frequency. If an AT-cut 16.777216 MHz quartz crystal is used,
by dividing the frequency by 512, then the desired frequency of 32.768KHz can be obtained.
The active implementation of the frequency divider is not difficult and is integrated within the oscillation IC.
Therefore, the 32.768 khz crystal oscillator achieved by using the AT-cut MHZ divider has a great improvement in frequency and temperature characteristics,
which can be achieved by maintaining a temperature frequency difference of ±30ppm or even ±20ppm at -40°C to 85°C without temperature compensation.
Summary
Compared to passive crystal oscillator, active crystal oscillator can reduce the need for tedious load matching,
thus greatly improving the stability of product performance.
